EMNLP-IJCNLP 2019 : WNGT workshop
Shared Task: Language Model Assisted Explanation Generation
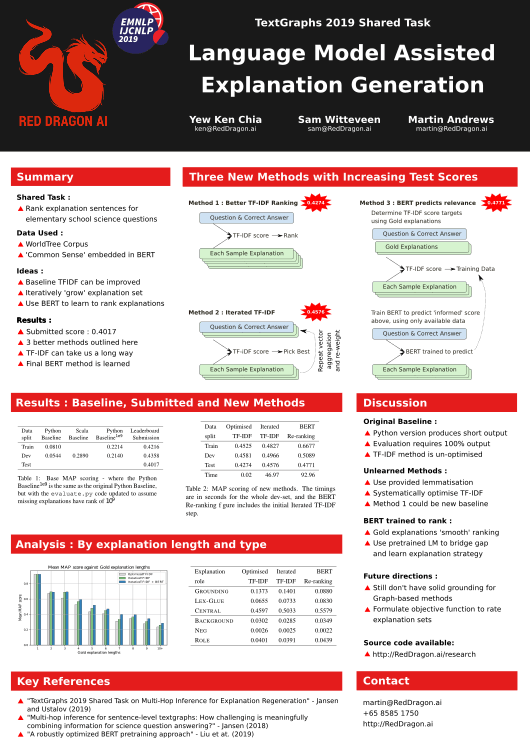
The TextGraphs-13 Shared Task on Explanation Regeneration asked participants to develop methods to reconstruct gold explanations for elementary science questions. Red Dragon AI's entries used the language of the questions and explanation text directly, rather than a constructing a separate graph-like representation. Our leaderboard submission placed us 3rd in the competition, but we present here three methods of increasing sophistication, each of which scored successively higher on the test set after the competition close.
EMNLP-IJCNLP 2019 : WNGT workshop
Paraphrasing with Large Language Models
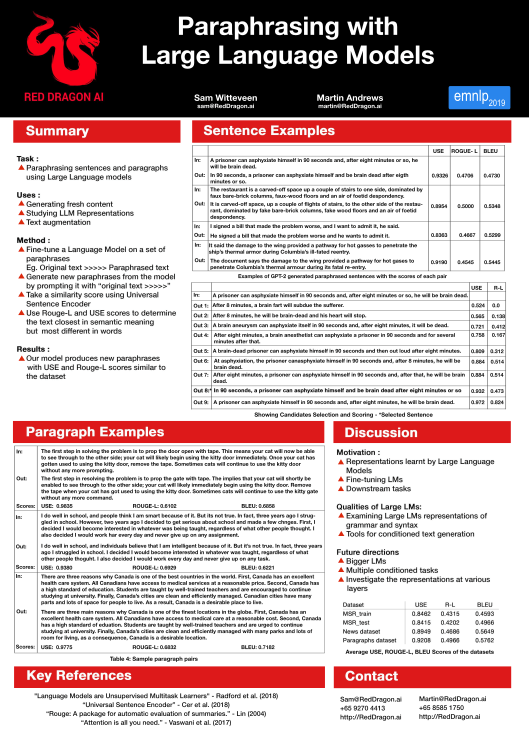
Recently, large language models such as GPT-2 have shown themselves to be extremely adept at text generation and have also been able to achieve high-quality results in many downstream NLP tasks such as text classification, sentiment analysis and question answering with the aid of fine-tuning. We present a useful technique for using a large language model to perform the task of paraphrasing on a variety of texts and subjects. Our approach is demonstrated to be capable of generating paraphrases not only at a sentence level but also for longer spans of text such as paragraphs without needing to break the text into smaller chunks.

EMNLP-IJCNLP 2019 : FEVER workshop
Unsupervised Natural Question Answering with a Small Model
The recent (2019-02) demonstration of the power of huge language models such as GPT-2 to memorise the answers to factoid questions raises questions about the extent to which knowledge is being embedded directly within these large models. This short paper describes an architecture through which much smaller models can also answer such questions - by making use of 'raw' external knowledge. The contribution of this work is that the methods presented here rely on unsupervised learning techniques, complementing the unsupervised training of the Language Model. The goal of this line of research is to be able to add knowledge explicitly, without extensive training.
NeurIPS 2018 : MLPCD2 workshop
Transformer to CNN: Improved Text Classification for Edge Devices
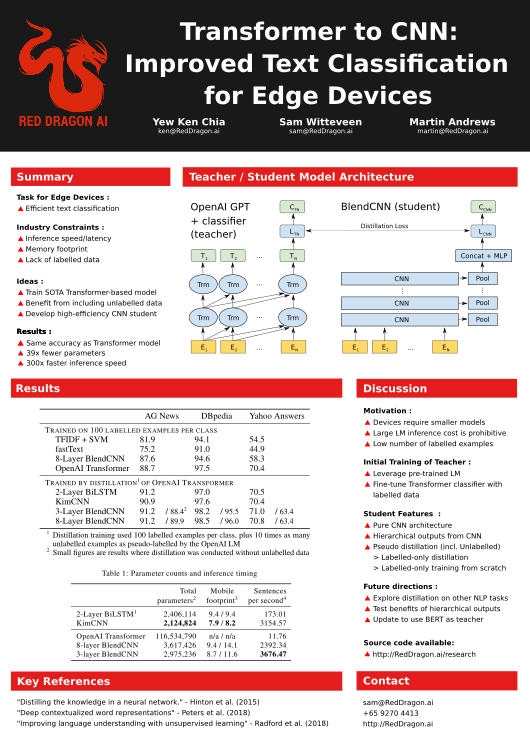
As Deep Learning and NLP models advance they also become more complicated and computationally heavy. This limits the ability of developers to use these models at the edge on phones and low power devices. In this paper, we introduce a new CNN architecture which can be trained by a distillation process from a large-scale model such as OpenAI's Transformer architecture. This student model is then small enough and fast enough to be run on phones. The model can then achieve 300x inference speedup and 39x reduction in parameter count and in some cases, the student model's performance surpasses its teacher on the studied tasks.
NeurIPS 2018 : ViGIL workshop
Scene Graph Parsing by Attention Graph
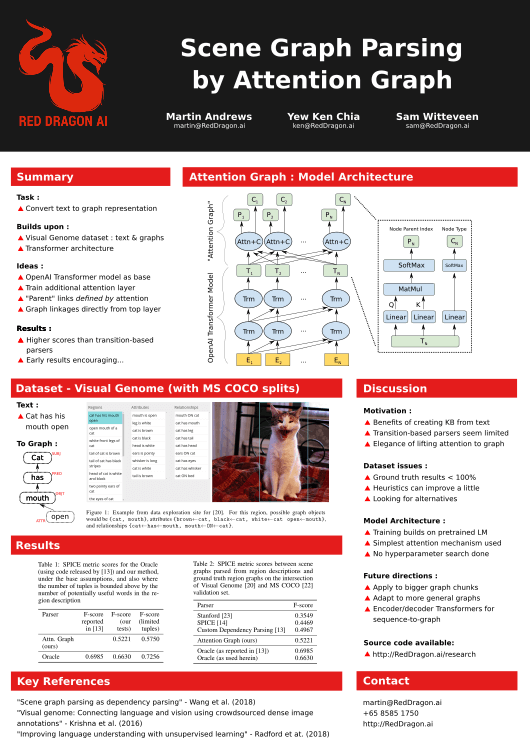
Scene graph representations, which form a graph of visual object nodes together with their attributes and relations, have proved useful across a variety of vision and language applications. Recent work in the area has used Natural Language Processing dependency tree methods to automatically build scene graphs. In this work, we present an `Attention Graph' mechanism that can be trained end-to-end, and produces a scene graph structure that can be lifted directly from the top layer of a standard Transformer model. The scene graphs generated by our model achieve an F-score similarity of 52.21% to ground-truth graphs on the evaluation set using the SPICE metric, surpassing the best previous approaches by 2.5%.
NeurIPS 2018 : MLOSS workshop
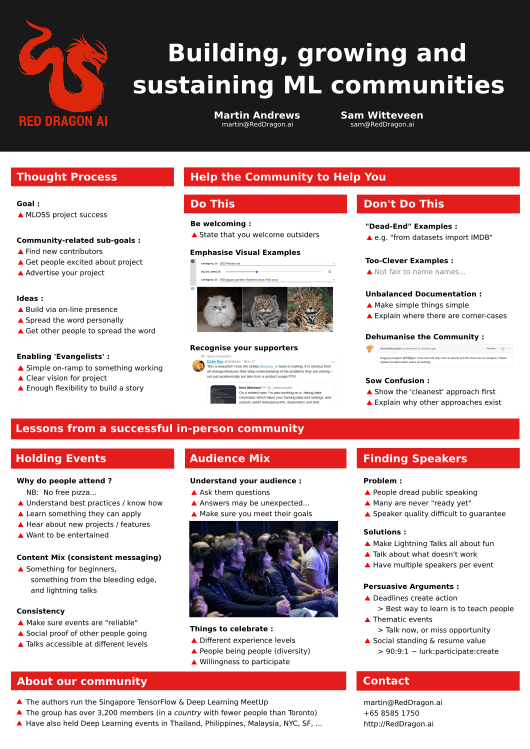
Building, growing and sustaining ML communities
While there are multiple research-based groups for the ML community around the world, the adoption of these skills by a broader base of developers will require new communities that reach beyond researchers to flourish at a large scale. The Singapore TensorFlow & Deep Learning community is a group of over 3,000 people from different backgrounds and levels that is pushing the adoption of ML in South-East Asia, via monthly in-person meetings, guest talks, and special events. In the proposed short talk, we will present some of the challenges, lessons learned and solutions found to building machine learning communities at scale.
NeurIPS 2018 : CDNNRIA workshop
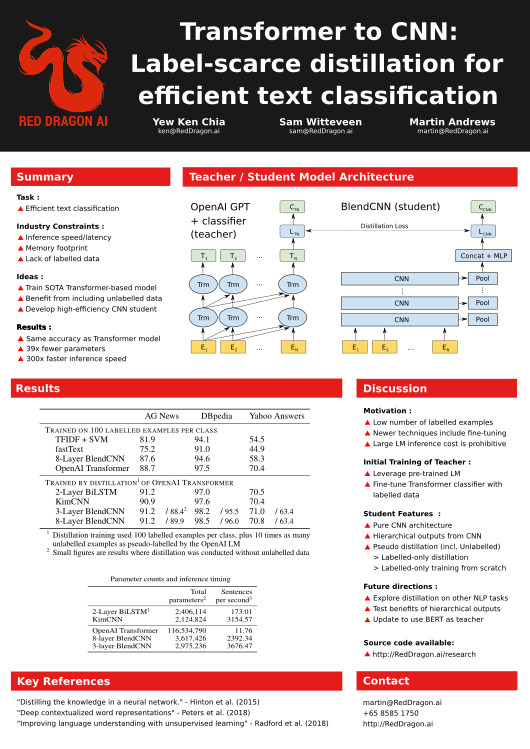
Transformer to CNN: Label-scarce distillation for efficient text classification
Significant advances have been made in Natural Language Processing (NLP) modelling since the beginning of 2018. The new approaches allow for accurate results, even when there is little labelled data, because these NLP models can benefit from training on both task-agnostic and task-specific unlabelled data. However, these advantages come with significant size and computational costs. This workshop paper outlines how our proposed convolutional student architecture, having been trained by a distillation process from a large-scale model, can achieve 300x inference speedup and 39x reduction in parameter count. In some cases, the student model performance surpasses its teacher on the studied tasks.
NIPS 2017 : ViGIL workshop
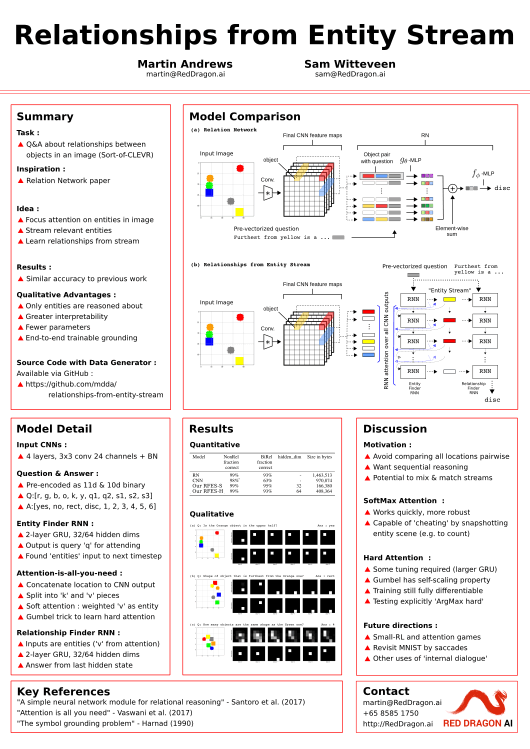
Relationships from Entity Stream
Relational reasoning is a central component of intelligent behavior, but has proven difficult for neural networks to learn. The Relation Network (RN) module was recently proposed by DeepMind to solve such problems, and demonstrated state-of-the-art results on a number of datasets. However, the RN module scales quadratically in the size of the input, since it calculates relationship factors between every patch in the visual field, including those that do not correspond to entities. In this paper, we describe an architecture that enables relationships to be determined from a stream of entities obtained by an attention mechanism over the input field. The model is trained end-to-end, and demonstrates equivalent performance with greater interpretability while requiring only a fraction of the model parameters of the original RN module.
